Introduction of the magnetic pivot
With this invention, Breguet not only overcame the negative effects of magnetism in a mechanical watch, but also succeeded in taming them to improve the pivoting, rotation and stability of the balance wheel axis.
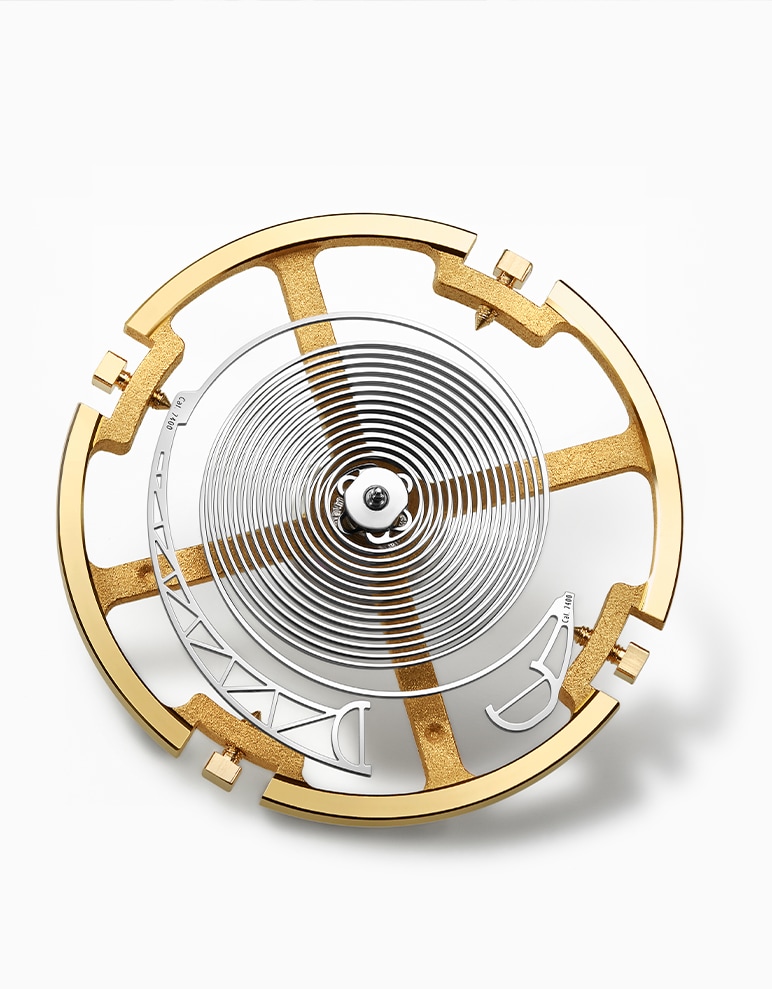
THE MAGNETIC PIVOT
With the patent of November 9, 2010 protecting the magnetic pivot, Breguet has set a new milestone in watchmaking history by using magnetism to improve the precision and the reliability of its timepieces. It is likely that the impact of this important invention will not be fully assessed for some years yet. The magnetic pivot consists of a carbon-steel balance staff and a ‘rare-earth’ magnet behind each endstone. One of the magnets is stronger than the other so that the balance-staff is in permanent contact with the endstone on the dial side and thus appears to be suspended.
Since the magnetic bond between the shaft and the endstone is stronger than the force of gravity, the shaft continues to pivot on the endstone irrespective of the position of the watch. Breguet’s advances in magnetism have also resulted in an unprecedented mechanism to improve the pivoting, rotation and the stability of the balance shaft. Furthermore, the system performs the role of a shock absorber. If a blow shifts the pivot out of position the magnetic attraction pulling it back increases with the extent of the pivot’s lateral displacement. The shaft thus returns automatically to its position, restoring the maximum magnetic flux.
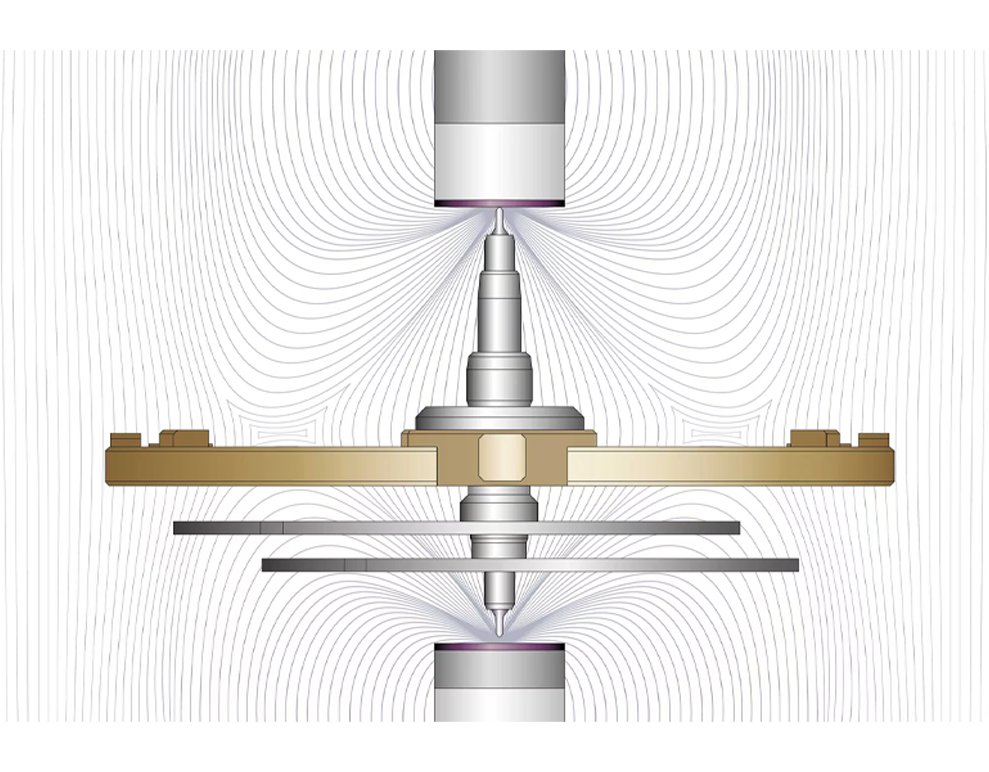

BALANCE-STAFF MORE STABLE
The magnetic field crossing through the balance-staff keeps the balance stable: it is immune to the low-intensity shocks ( the most frequent type ) as well as the accelerations to which the watch is subjected. It returns almost instantly to its correct position after stronger accidental shocks. The performance of the balance is thus much enhanced since it does not have to contend with the friction of a conventionally pivoted balance, particularly in a vertical position.
Magnetic induction brings many advantages to the ratekeeping of the movement. The balance-staff is placed in the magnetic field and held against the endstone due to the magnetic flux that also tends to bring the staff back to its optimal position.